Battery-electric cars don’t use any gasoline, but instead run solely on electricity stored in a battery pack that energizes one or more electric motors and produces zero tailpipe emissions. These cars can be charged most anywhere, anytime and usually at a much lower cost than fueling with gasoline. Their driving ranges on a full charge vary widely from about 100 to more than 500 miles, with considerably higher ranged electric cars coming soon.
Benefits
- Fun to drive
- Quiet
- Quick off the line
- Convenient to recharge
- No trips to the gas station
- Wake up with a full “tank”
- High-tech
- Cheaper to operate and maintain
- Zero emission
- Access to carpool lanes and other incentives
How They Work
Currently, most electric cars are powered by rechargeable lithium-ion batteries that are compact and have a very high energy density. They are charged primarily by an external electricity source, which can be as simple as a standard 120-volt outlet. The onboard charger takes the incoming alternating current (AC) electricity and converts it to direct current (DC) power for charging the main battery. The power is delivered to what is called the electric traction motor that drives the car’s wheels. A variety of sophisticated electronic components are involved in the process.
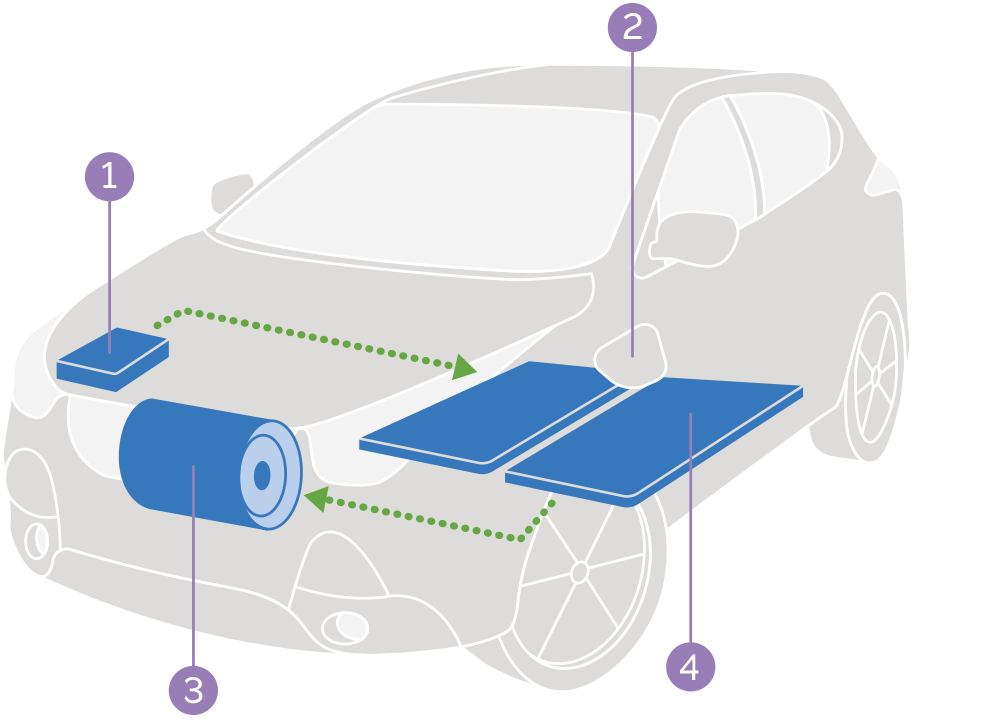
- Onboard Charger – Converts incoming AC electricity to DC power for charging the battery
- Charge Port – Enables the car to be plugged in to an external power source to charge the battery
- Electric Motor – Powered from the battery, the electric motor propels the car at all times
- Battery – Typically positioned below the seats for better weight distribution, these batteries can be as large as 100kWh and power the electric motor
Availability
There are more than 120 makes and models of electric cars available with many more coming soon. These cars come in a variety of sizes and price points. Search vehicles to see available models.
Performance
Electric cars are powerful, with quick acceleration, great torque and a quiet drive.
Costs
Although electric cars have a higher upfront cost than conventional cars there are a variety of incentives and lease options to help reduce these costs and allow drivers to upgrade to newer technologies faster. Electric car charging in California costs roughly half the price of powering a standard gasoline car for driving the same distance.
Electric cars don’t need oil changes, fuel filters or smog checks and due to regenerative braking, brake pads last longer. When you buy or lease an electric car, you won’t have to worry about replacing the battery any time soon since they come with extended battery warranties, with most covering 8-10 years and 100,000 or unlimited mileage.
Incentives
Electric cars are eligible for a variety of federal, state and local incentives, such as the Clean Air Vehicle decal, California’s Clean Vehicle Rebate Project and programs to support clean transportation ownership in low-income and disadvantage communities. To find incentives in your region, visit incentive search.
Charging
Electric cars are charged by plugging in to an electrical power source, ranging from a standard 120-volt or 240-volt circuit, to commercial-grade charging stations. A small amount of charging takes place while driving by a process that converts kinetic energy produced by braking to electricity, known as regenerative braking.
Most drivers plug in at home and charge overnight to wake up to a full charge. Increasingly, charging stations are found at shopping areas, parking lots, public destinations and workplaces.

Charging equipment is classified in three levels depending on their capacity and rate of charging.
- Level 1 charging uses a cord set provided with the car that plugs directly into a 120-volt outlet, supplying about 40 miles of electric driving per eight hours of charging.
- Level 2 charging uses 208-volt (commercial) and 240-volt (residential) service and typically requires a dedicated 40-amp circuit. They deliver about 14-35 miles of range per one hour of charging.
- DC Fast Charging is the quickest way to refuel an electric car and can provide up to 100 miles of range in about 30 minutes. The number of DC Fast Charging stations is increasing as well as the speed these chargers can charge a car.
elrhb